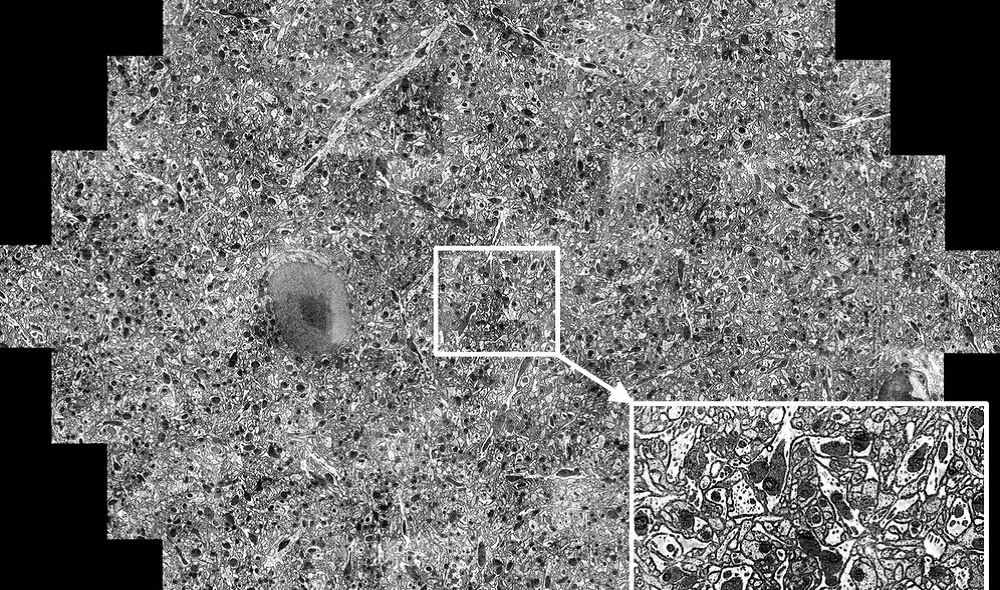
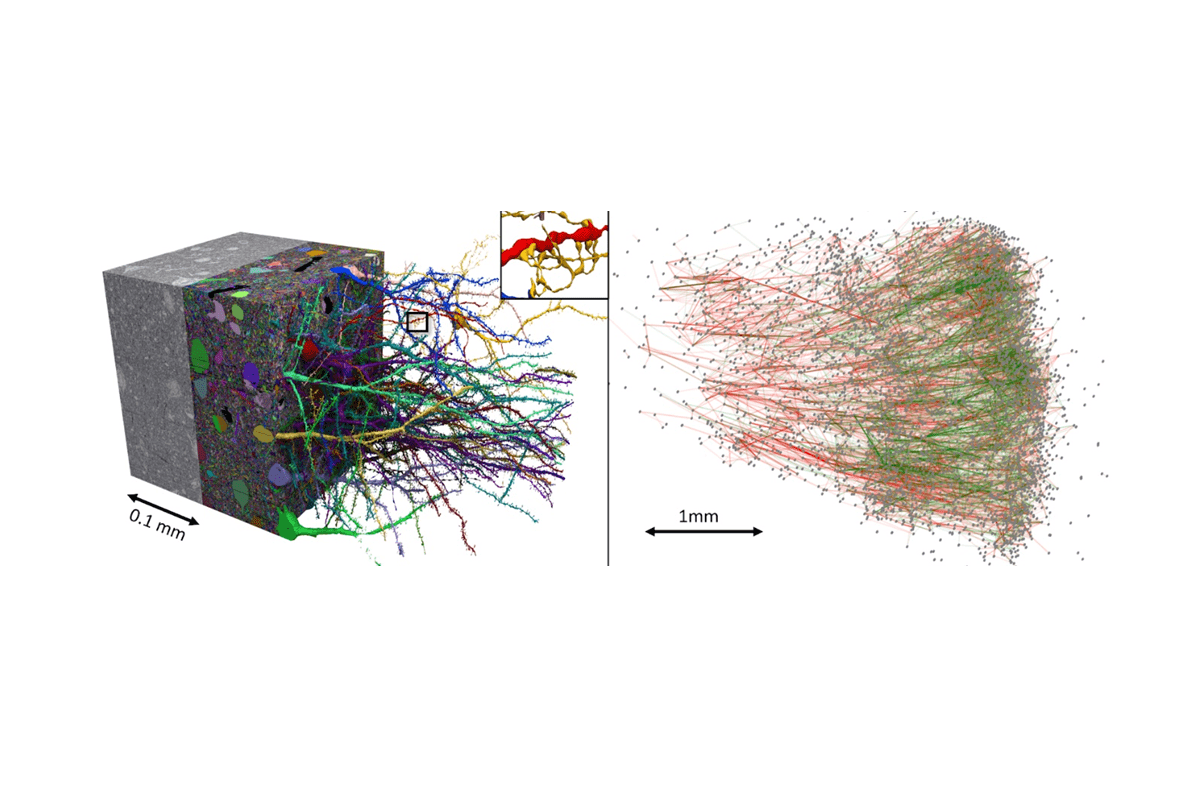
Two recent papers (June 2021) by groups in the USA have shown how a multi-beam electron microscope such as the MultiSEM from Zeiss, when combined with the automated ultramicrotome preparation of serial sections and powerful image segmentation algorithms can provide unprecedented data about how neurons in the brain connect to provide function – examples of the research area known as ‚connectomics‘.
NanoWorldMaps will become a distributed research infrastructure with internationally distributed imaging nodes, each equipped with a common sub-set of sample preparation and microscopy techniques, including a multi-beam scanning electron microscope, but also complementary microscopy instrumentation e.g. Raman or SIMS for chemical information, or fluorescence microscopy for protein mapping. Additional domain-specific techniques are also likely. Each node would include specialist staff. Users of the imaging service would be supported by specialists in image processing.
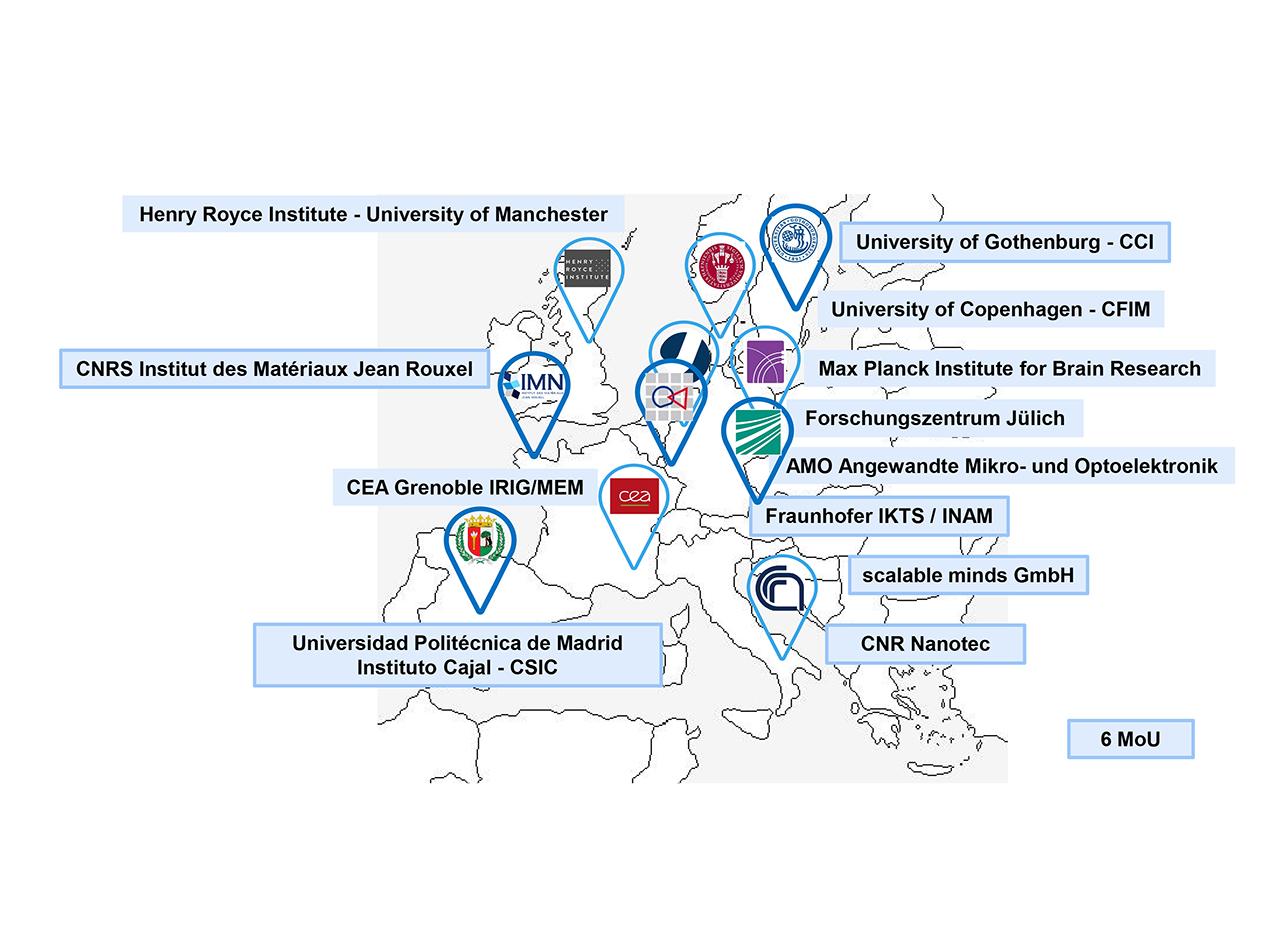
NanoWorldMaps members have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to support the concept and implementation phase and build a preliminary governance structure. Scientists from academia and industry will benefit from NanoWorldMaps by using open access to cutting-edge 2D/3D imaging technologies combined with pre-defined processes for sample preparation, image acquisition, and data analysis. Microscopy core facilities and centers can profit by becoming one of the distributed NanoWorldMaps nodes.
NanoWorldMaps will enable Ultra-Fast and Extra-Large Area 2D/3D Imaging for material and life scientists
About NanoWorldMaps
NanoWorldMaps works on empowering Europe to lead the revolution in high-throughput multimodal imaging at the nanometer scale. NanoWorldMaps will become a distributed European Research Infrastructure to provide cutting-edge enabling technologies such as Multi-Beam Scanning Electron Microscopy as a service. NanoWorldMaps services will be focused on the needs of scientists from academia and industry in a growing list of strategic application areas.
Literature and image sources
- A Browsable PetascaleReconstruction of the Human Cortex by A Shapson-Coe et al. (J W Lichtman group at Harvard University), with this associated blog entry from Google
- Double cones and the diverse connectivityof photoreceptors and bipolar cells in an avian retina, A Gunther et al. Journal of Neuroscience, 2021.
- Image source: A connectomic study of a petascale fragment of human cerebral cortex. Preprint available at bioRxiv: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.05.29.446289